受益于苹果的封闭生态,开发者常常不必关注太多的底层细节,就能做出界面美观,性能优良的App,当然其中Apple也大方的开放出了少许的源码,例如Runtime源码,感谢http://blog.csdn.net/wotors/article/details/54426316 提供了可以编译成功的源码工程。
+load()
我们来通过源码来探讨一下load方法的加载时机,和在父类,Category中的加载顺序
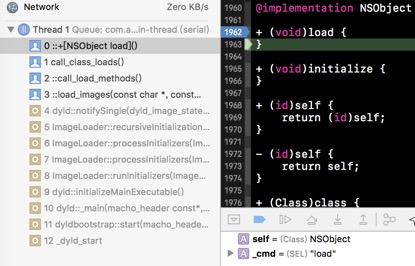
首先我们在+load方法中打上断点,看到如下的执行过程
通过runtime的源码我们可以找到load_images方法的具体实现,代码如下
1 | /*********************************************************************** |
在这里我们可以发现两个关键的方法,prepare_load_methods(…) call_load_methods()
1 | void prepare_load_methods(const headerType *mhdr) |
1 | static void schedule_class_load(Class cls) |
其中我们在void prepare_load_methods(const headerType *mhdr)方法中明显可以看出,先处理Class的相关信息,后处理Category的相关信息,在处理Class时会进入到static void schedule_class_load(Class cls)方法中,在此方法中会递归的寻找到父类,然后调用其add_class_to_loadable_list(cls)的信息
1 | void add_class_to_loadable_list(Class cls) |
在这里判断了Class中是否实现了+load方法,若实现了把该Class顺序存储到loadable_classes中,Category同理也调用了相关方法,将实现的load方法的category添加到了list中,如下图
1 | /*********************************************************************** |
到这里prepare_load_methods(…)这个方法的使命就算结束了,我们找到了可以执行load方法的Class和Category,接下来让我们看一下执行的步骤
1 | void call_load_methods(void) |
关键方法 call_class_loads() call_category_loads(),可以看出是先执行的Class中的load方法,再执行Category中的load方法,下面是两个方法的具体实现
1 | /*********************************************************************** |
1 | /*********************************************************************** |
总结
+load方法通过函数指针调用,而不是objc_msgSend
+load方法的调用时机是在Runtime初始化的时候,其中的调用顺序是父类->子类->分类,其中默认调用一次,在Class中和Category中都实现了load方法,则在两者之间都会调用,且在子类实现+load方法时不需要显示的调用[super load]